Classes
基础知识
类的意义是什么——抽象以及资源管理。
C++语言的核心特性就是class
C++语言的大多特性都是为了更好地设计类而生的
问题
- 如何对C++的class进行深入实践?
- OOP课程
- 继续学习
具体类型,抽象类型
具体类型
- 如同内置类型的类型
- 类型的表示只是其定义的一部分;比如vector,我们说的vector指的是其指向其内部存储的一个指针
- 如果需要更改具体类型的结构,必须要经过重新编译
- 资源管理对象(resource handler)也是其中一种(vector, string)
算术类型
典型的用户定义算数类型是复数
c++
class complex {
double re, im;
public:
complex(double r, double i):re{r}, im{i}{}
complex(double r):re{r}, im{0} {}
complex():re{0}, im{0}{}
double real() const { return re; }
void real(double d) { re = d; }
double imag() const { return im; }
void imag(double d) { im = d; }
complex& operator+=(complex z)
{
re += z.re; // add to re and im
im += z.im;
return *this; // and return the result
}
complex& operator-=(complex z)
{
re -= z.re;
im -= z.im;
return *this;
}
complex& operator *= (complex z); // defined out-of-class somewhere
complex& operator /= (complex); // defined out-of-class somewhere
}这里有两个值得注意的问题:
- const方法与作用对象的问题
- a += b 和 a= a+ b的区别
c++
complex z = {1,0};
const complex cz {1,3};
z = cz;
// OK: assigning to a non-const var iable
cz = z;
// error : complex::operator=() is a non-const member function
double x = z.real();
// OK: complex::real() is a const member functionc++
foo += 1;
//实际上等于(foo得是非原生类型):
foo.operator+=(1);
foo = foo + 1;
//上述内容实际上等于
temp = foo.operator+(1);
foo.operator=(temp);用户定义的运算符(重载运算符)应该要谨慎地使用。
容器类型
容器是元素的集合。
c++
class Vector {
public:
Vector(int s):elem{new double[s]}, sz{s} // constr uctor: acquire resources
{
for (int i=0; i!=s; ++i) // initialize elements
elem[i]=0;
}
~Vector() { delete[] elem; } // destr uctor: release resources
double& operator[](int i);
int size() const;
private:
double* elem; // elem points to an array of sz doubles
int sz;
};- 容器类型的构造函数和析构函数分别承担了分配内存,给定初始值以及销毁对象并释放内存的作用;
- 分配动态空间的方法是
new运算符,与之对应,释放内存的运算符是delete(普通对象)和delete[](销毁array); 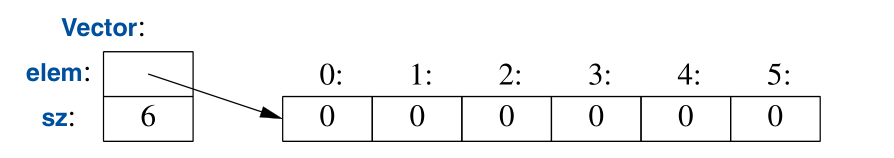
- 尽量不要在代码中直接使用new和delete运算符(naked new/naked delete)
抽象类型
虚数,向量之所以被称为具体类型,是因为它们的表现是定义的一部分。而与之相对,抽象类型,将其表现完全与实现分离。
c++
class Container {
public:
virtual double& operator[](int) = 0;
virtual int size() const = 0;
virtual ~Container() {}
}对比一下,Python,Go语言的抽象类型
go
type Container interface{
AccessByIndex(index int) float64
Size() int
}python
from abc import ABCMeta, abstractmethod
import gc
class Container:
"""
Abstract Class
"""
__metaclass__ = ABCMeta
def __init__(self):
self.collection = list()
@abstractmethod
def __getitem__(self, item):
pass
@abstractmethod
def __len__(self):
pass
def __del__(self):
del self.collection
gc.collect()
class Array(Container):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def __getitem__(self, item):
return self.collection.__getitem__(item)
def __len__(self):
return self.collection.__len__()
def push_back(self, ele):
self.collection.append(ele)上面的代码定义了一个抽象类<容器>
- virtual代表这个方法将会在子类中被重新定义,加上该关键字的函数被称为虚函数
- Container的子类要实现对应的接口,具体的,当看到"=0"这项语法,说明该子类必须定义这项方法
- 因此,你不可能直接define一个"Container"对象
- 拥有纯虚函数的类因此被称为抽象类
子类
c++
class Vector_container : public Container { // Vector_container implements Container
public:
Vector_container(int s) : v(s) {} // Vector of s elements
~Vector_container() {}
double& operator[](int i) override {return v[i];}
int size() const override {return v.size();}
private:
Vector v;
};- Container和Vector_container的关系就是父类/超类和子类的关系
- : public代表的是继承于
- 具体的实现给到override关键字是一个好的习惯(也就是你可以不给),可以防止拼写错误等问题
问题
- Python中的list和CPP的vector对比;
- 实现复数的乘法和除法;
- +=;++运算符的使用选择;
- 如何使用字面量定义算数类型;
- 大整数算数类型的定义,实现,测试;
- https://github.com/sercantutar/infint/blob/master/InfInt.h
- Python,Go语言中的抽象类型
- Array对象的实现